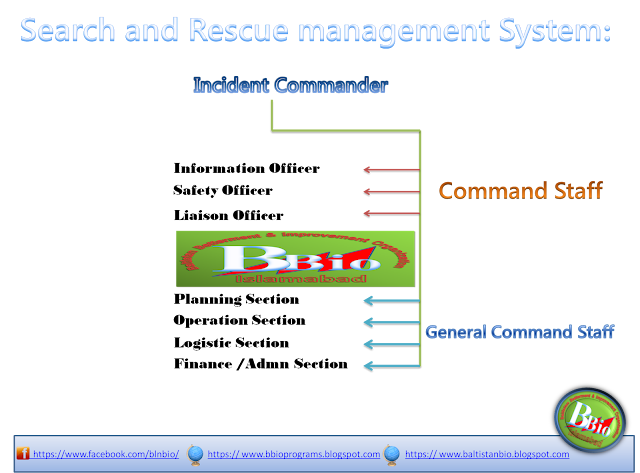
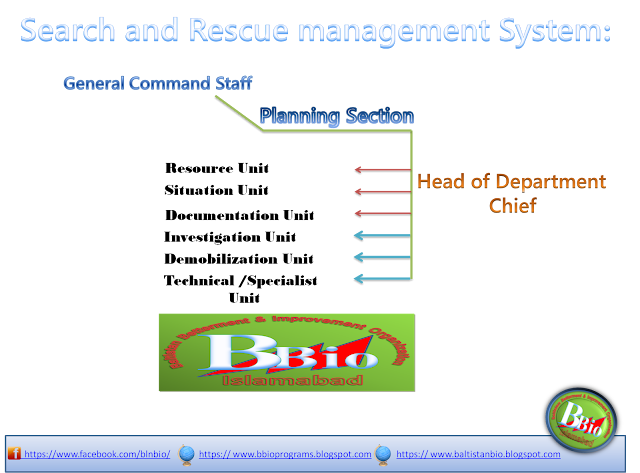
Incident Management:-
The main principle of incident management is that you are the most important person and your safety comes first! Your first actions when coming across the scene of an incident should be:
§ Check for any dangers to yourself or bystanders
§ Manage any dangers found (if safe to do so)
§ Ensure continuing safety of yourself and bystanders
As a first aider it is important to have a good understanding of infection control. Infection control is an important for two reasons:
ü To protect yourself! Remember you are the most important person
ü To protect the patient
Think about the following situation:
And
Think about the following questions:
• What would your first action be?
• What dangers could there be in this situation?
• How would you manage these dangers?
• Which other emergency services would be required?
In some situations it may be too dangerous for you to approach the scene. In this situation you should remember that you are the most important person – stay back and call for professional assistance.
right-1_AdSense1_1x1_as
In many first aid situations, help from the emergency services may be required.
Ensure you know which number to call!
– Fire & Rescue Islamabad 16
– CDA CARE: 1122
– Punjab Emergency Service: 1122
– Police Rescue Service: 15
– Edhi Ambulance: 115
– All Pakistan Fire Brigade: 16
Give clear, precise information about
• -The location of the incident
• – The number of casualties / people involved
• – The nature of their injuries
• – In some cases, their age
• – Any hazards at the incident (e.g: spilt fuel, fire, electricity)
Note: If the area is remote/difficult to access, consider sending someone to meet the emergency services in a known location.